Is a medium through which information usually
moves from one network device to another.
TYPES OF CABLES
*use current
- Unshielded
Twisted Pair (UTP) cable
- Shielded
Twisted Pair (STP) cable
*use light
- Co-axial
cable
- Fiber
Optic cable
- Wireless
cable
UNSHIELDED
TWISTED PAIR (UTP) CABLE
-has 4 pairs of wires inside jacket
-each pair is twisted with different number of
twists per inch
-to help eliminate interference from adjacent pairs
(nearest disruption) & others electrical devices.
-UTP’s categories:
TYPES
|
USE
|
EXAMPLE
|
Category 1
|
Voice
|
Telephone
wire
|
Category 2
|
Data to 4
Mbps
|
Local talk
|
Category 3
|
Data to 10
Mbps
|
Ethernet
|
Category 4
|
Data to 20
Mbps
|
16 Mbps
token ring
|
Category 5
|
Data to 100 Mbps
|
Fast
ethernet
|
# category 3 & 4 usually use in school.
-Standard connecter : RJ-45 connecter (Registered
Jack)
-Disadvantages : it may be susceptible to radio
& electrical frequency
interference.
SHIELDED
TWISTED PAIR (STP) CABLE
-consist of
two individual wires wrapped in a foil shielding
-to help
provide a more reliable (no disruption/accurate) communication
-suitable for
environments with electrical interference
-extra
shielding can make cables quite bulking
-often
used on networks using Token Ring topology
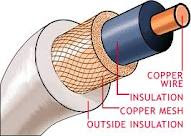
CO-AXIAL CABLE
-has a single copper conductor at its center
-a plactic layer provides insulation between center conductor
& a braided metal shield
-metal shield: helps to
block any outside interference from fluorescent lights, motors, and other
computers
-connecter: Bayone-Neill-Concelman
(BNC) connector
-different types of adapters
are available for BNC connectors, including a T-connector, barrel connector,
and terminator.
FIBER OPTIC CABLE
-consists of a center
glass core surrounded by several layers of protective materials
-it transmits light rather
than electronic signals
-able to transmit signals
over much longer distances than coaxial and twisted pair
Summary of Ethernet cabling.